前言
服务器时间同步有多种情况,不同情况处理方式也有差异。比如,可以连外网,则可直接使用ntpdate定时同步互联网的时间服务器时间(如阿里的时间服务器ntp.aliyun.com)。
如果不能连外网,则需要指定一台服务器当作时间服务器。再由其他内网服务器作为客户端从时间服务器同步时间。
同步互联网时间
1、安装ntpdate
# yum -y install ntpdate
2、添加定时任务
# crontab -e
加入以下内容

|
0 */12 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate -u ntp.aliyun.com > /dev/null 2>&1; /sbin/hwclock -w |
表示每12小时执行一次同步,时间可按实际情况修改。
至此,定时同步配置完成。当然也可以单独执行ntpdate -u ntp.aliyun.com,执行一次时间同步。
内网环境时间同步
时间服务器搭建
- 安装ntp
# yum -y install ntp
# vi /etc/ntp.conf
![]()
|
修改内容 |
说明 |
|
restrict 192.168.235.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap |
表示允许同一网段的客户端来同步时间 restrict 对ntp做权限控制 ignore:忽略所有类型的NTP连接请求 nomodify:限制客户端不能使用命令ntpc和ntpq来修改服务器端的时间 noquery:不提供NTP网络校时服务 notrap:不接受远程登录请求 notrust:不接受没有经过认证的客户端的请求 192.168.235.0表示子网IP,255.255.255.0表示子网掩码 |
|
server 127.127.1.0 |
添加本机为时间服务器 |
|
fudge 127.127.1.0 startum 10 |
时间服务器层级0-15 0表示顶级 10通常用于给局域网主机提供时间服务 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
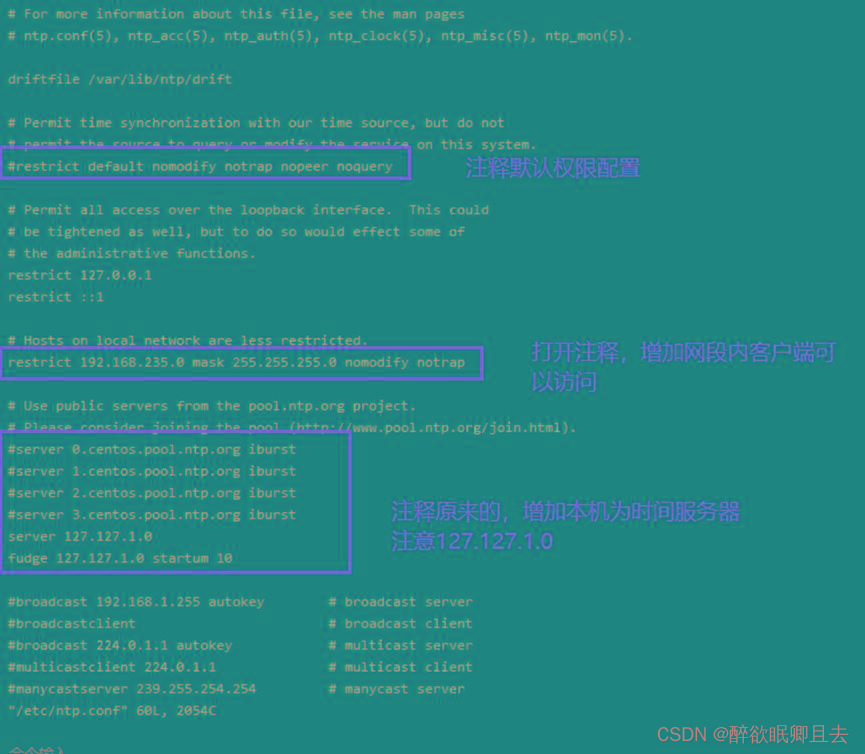
配置完成后保存。
- 加入开机启动
# systemctl enable ntpd
![]()
- 启动ntpd
# systemctl start ntpd
![]()
- 可以查看状态
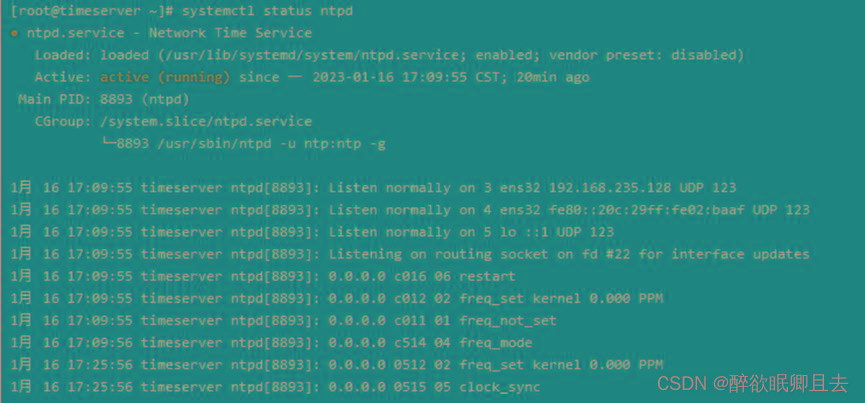
# systemctl status ntpd
相关命令
|
命令 |
说明 |
|
systemctl enable ntpd |
加入开机启动 |
|
systemctl start ntpd |
启动ntpd |
|
systemctl restart ntpd |
重启ntpd |
|
systemctl stop ntpd |
停止ntpd |
|
systemctl status ntpd |
查看状态 |
|
|
|
客户端同步配置
客户端的配置有两种,一种是参照互联网时间同步的方式,另一种是使用ntp同步。
ntpdate方式
这种方式简单明了,直接暴力
- 安装ntpdate
# yum -y install ntpdate
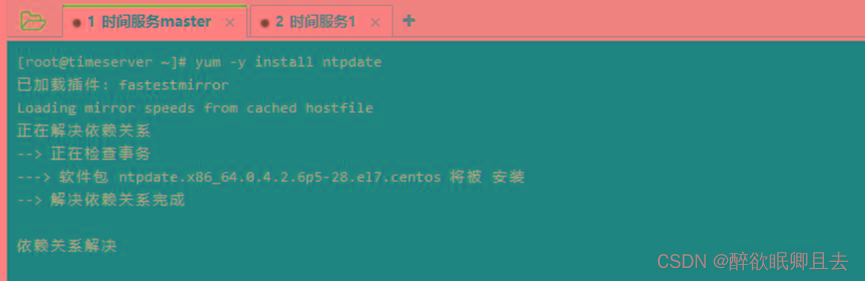
- 添加定时任务
# crontab -e
加入以下内容

|
0 */12 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate -u 192.168.235.128> /dev/null 2>&1; /sbin/hwclock -w |
ntp客户端方式
- 安装ntp
# yum -y install ntp
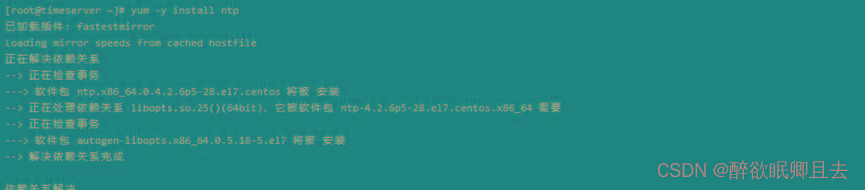
- 编辑配置文件
Ntpd服务器和客户端都采用同一个配置文件
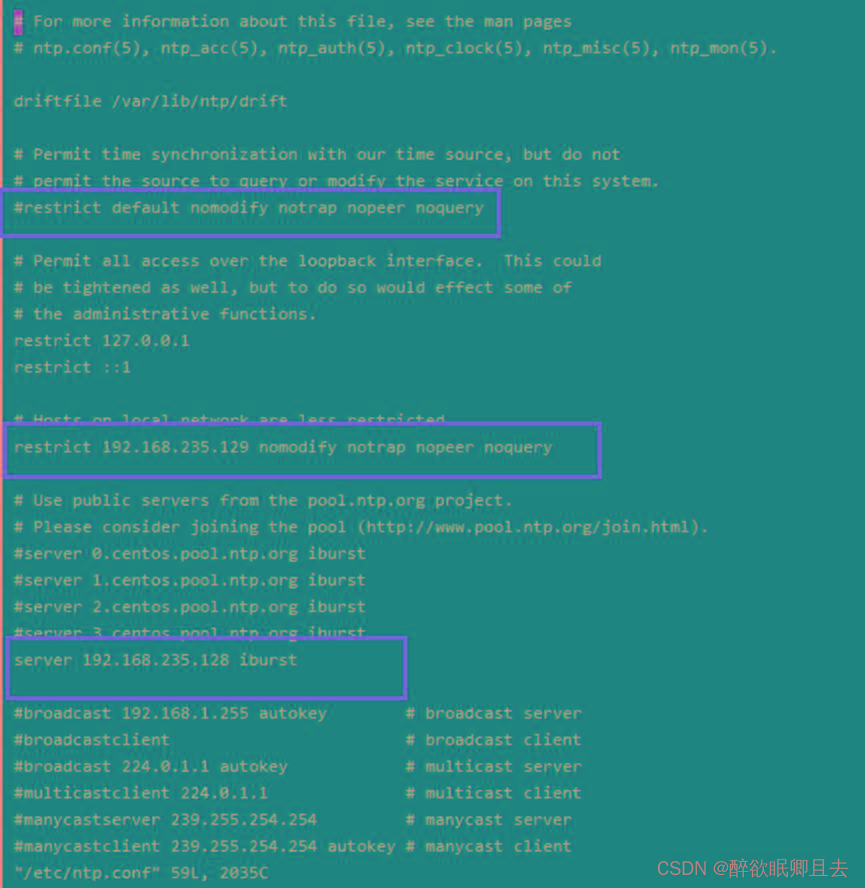
# vi /etc/ntp.conf
![]()
|
修改内容 |
说明 |
|
restrict 192.168.235.129 nomodify notrap nopeer noquery |
表示不允许本机修改时间 restrict 对ntp做权限控制 ignore:忽略所有类型的NTP连接请求 nomodify:限制客户端不能使用命令ntpc和ntpq来修改服务器端的时间 noquery:不提供NTP网络校时服务 notrap:不接受远程登录请求 notrust:不接受没有经过认证的客户端的请求 192.168.235.0表示子网IP,255.255.255.0表示子网掩码 |
|
server 192.168.235.128 iburst |
添加192.168.235.128(前面配置的服务器)为时间服务器 |
|
|
|
- 加入开机启动
# systemctl enable ntpd
![]()
- 启动ntpd
# systemctl start ntpd
![]()
- 可以查看状态
# systemctl status ntpd
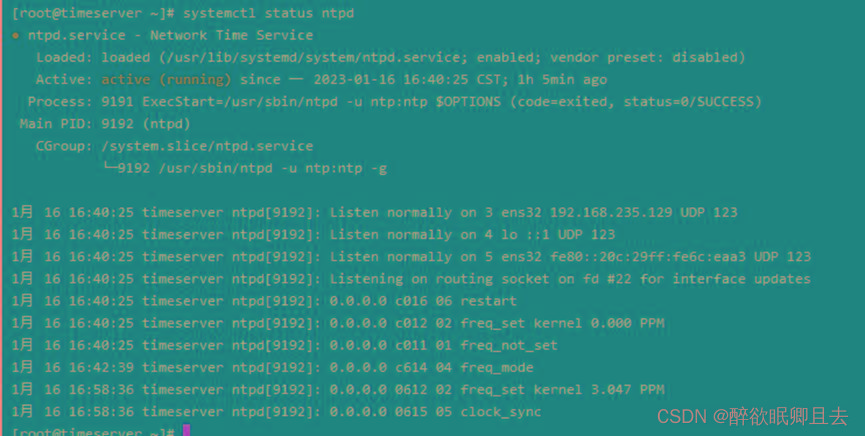
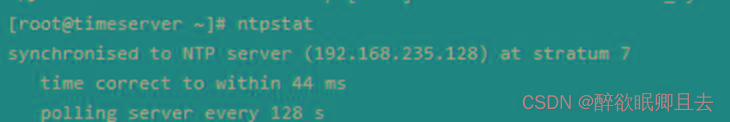
也可以用ntpstat查看
# ntpstat
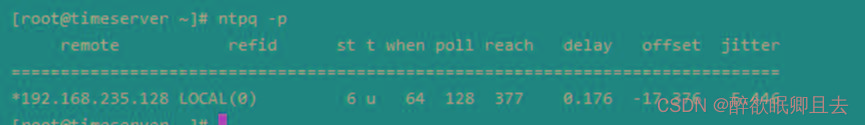
用ntpq -p查看,详细同步信息
# ntpq -p
|
remote |
时间服务器 |
|
st: |
即stratum阶层,值越小表示ntp serve的精准度越高; |
|
when |
单位秒,几秒前曾做过时间同步更新的操作; |
|
poll |
每隔多少秒与ntp server同步一次 |
|
reach |
已经向上层NTP服务器要求更新的次数; |
|
delay |
网络传输过程钟延迟的时间 |
|
offset |
时间补偿的结果 |
|
jitter |
Linux系统时间与BIOS硬件时间的差异时间 |
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u011048844/article/details/131192079