概述
我们今天主题主要是针对一些简单的优化, 我们拿到一个慢sql,首先就是先explain看一下大概情况,其中有一栏Extra中,有三个值我们需要注意一下,也是我们最常见的三个值,分别是Using where Using index Null Using intersect
案例
//表结构
create table test.user
(
id int auto_increment
primary key,
user_id int not null,
children_id int not null,
create_time datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP null,
update_time datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP null
);
//sql语句
select * from user where user_id=2 and children_id=7 ;
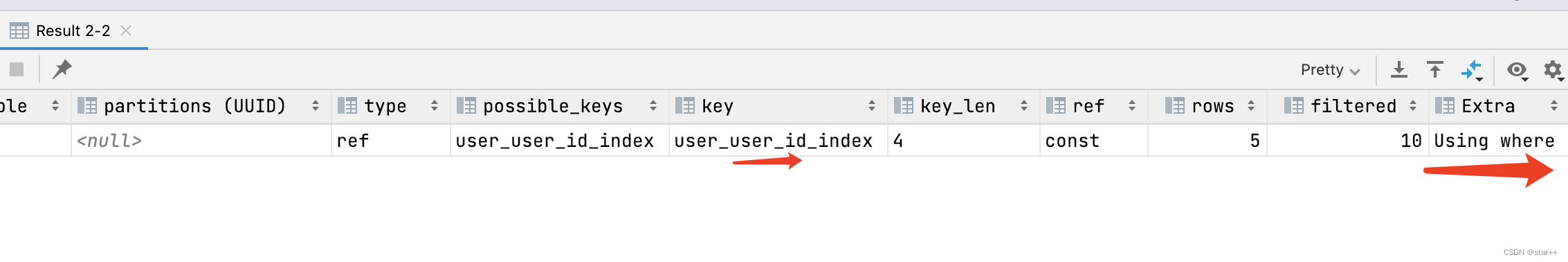
Using where(给and的一个字段加索引)
explain select * from user where user_id=2 and children_id=7 ;
Null(给and的两个字段加联合索引)
explain select * from user where user_id=2 and children_id=7 ;
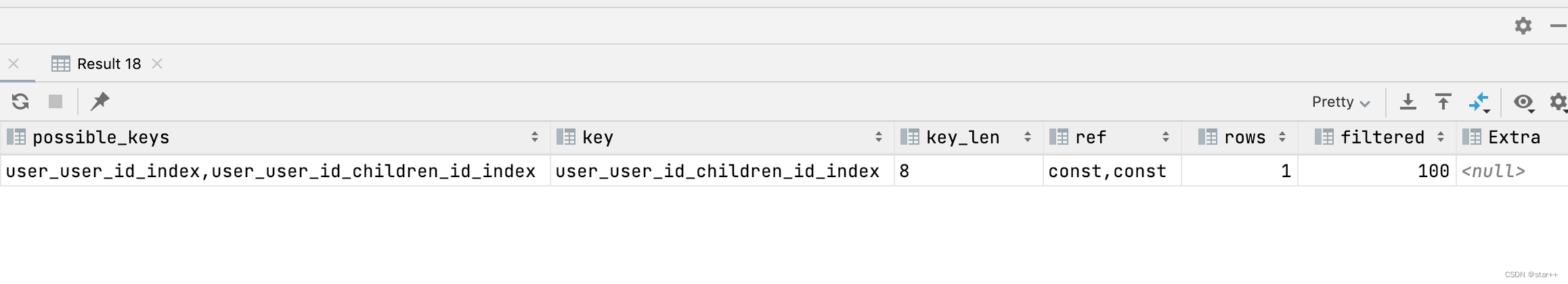
Using index
explain select user_id from user where user_id=2 and children_id=7 ;

Using intersect(给and的每一个字段单独加索引)
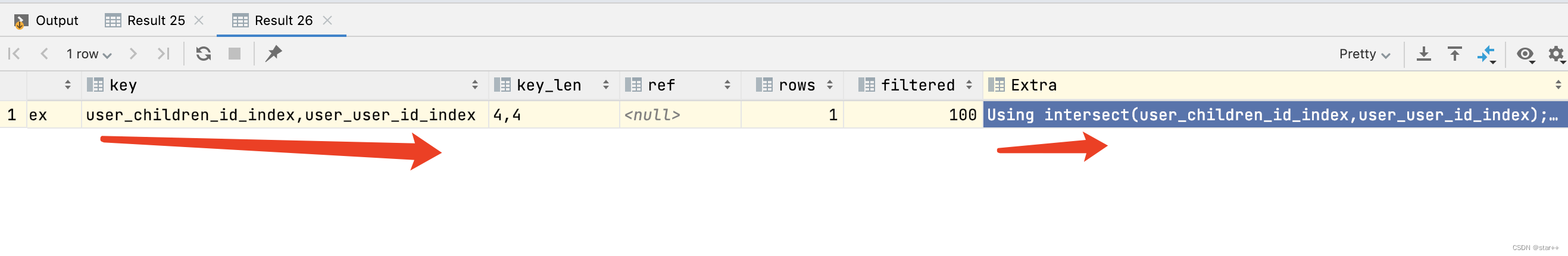
说明: 这种情况下,其实是mysql使用了索引合并的优化手段,其作用类似于上面的联合索引.介于Using where 和Null之间
总结
1.效率上来讲 Using index>Null>Using intersect>Using where
2.一般情况下,如果走了Using intersect,一般建议两个字段可以建立联合索引了
3.Using intersect又称索引合并, 是mysql认为这两个字端比较有辨识度的情况下才会帮你优化成这种方案,其实我理解就是mysql就是暗示你可以建立联合索引了
4.可见,联合索引在一些情况下,可以大大提高效率
5.按照mysql检索语句执行,一般只会设计一颗B+树,其他查询使用Using where来扫描剩下条件进行逐一筛选. Using intersect是唯一一种情况会操作两颗B+树.
6.这里也并不是建议and条件全都建立一个联合索引,一定是辨识度高的几个字段建立联合索引,其他剩下的数据不多,后面的条件走Using where也无所谓
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「star++」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38312719/article/details/127222920