netty分布式服务如何实现
在说nettty分布式之前,首先说下,netty是基于nio编程的,如果大家对nio不熟悉还是先看下nio相关的知识。
netty的线程模型和核心组件
1:netty的线程模型
netty通过Reactor模型基于多路复用器接收并处理用户请求(能讲就多讲一点),内部实现了两个线程池,boss线程池和work线程池,其中boss线程池的线程负责处理请求的accept事件,当接收到accept事件的请求时,把对应的socket封装到一个NioSocketChannel中,并交给work线程池,其中work线程池负责请求的read和write事件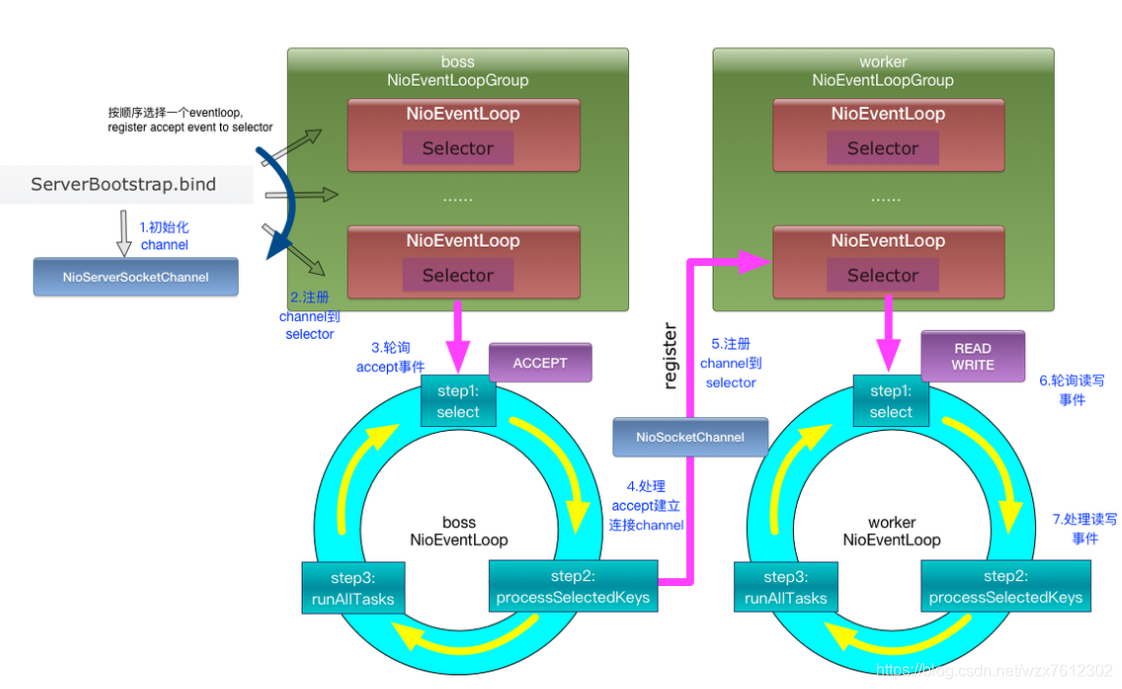
2.Netty核心组件
Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap:Netty应用程序通过设置bootstrap引导类来完成,该类提供了一个用于应用程序网络层配置的容器。Bootstrap服务端的是ServerBootstrap,客户端的是Bootstrap。
Channel:Netty 中的接口 Channel 定义了与 socket 丰富交互的操作集:bind, close, config, connect, isActive, isOpen, isWritable, read, write 等等。
ChannelHandler:ChannelHandler 支持很多协议,并且提供用于数据处理的容器,ChannelHandler由特定事件触发, 常用的一个接口是ChannelInboundHandler,该类型处理入站读数据(socket读事件)。
ChannelPipeline:ChannelPipeline 提供了一个容器给 ChannelHandler 链并提供了一个API 用于管理沿着链入站和出站事件的流动。每个 Channel 都有自己的ChannelPipeline,当 Channel 创建时自动创建的。 下图说明了ChannelHandler和ChannelPipeline二者的关系: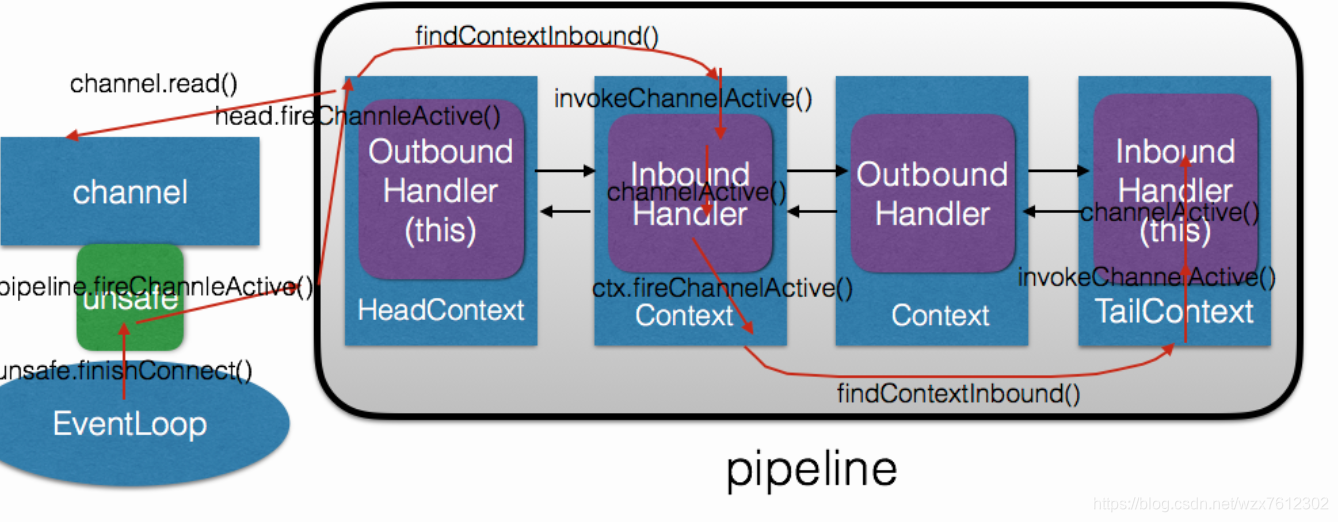
EventLoop:EventLoop 用于处理 Channel 的 I/O 操作。一个单一的 EventLoop通常会处理多个 Channel 事件。一个 EventLoopGroup 可以含有多于一个的 EventLoop 和 提供了一种迭代用于检索清单中的下一个。
ChannelFuture:Netty 所有的 I/O 操作都是异步。因为一个操作可能无法立即返回,我们需要有一种方法在以后获取它的结果。出于这个目的,Netty 提供了接口 ChannelFuture,它的 addListener 方法
Netty 是一个非阻塞、事件驱动的网络框架。Netty 实际上是使用 Threads( 多线程) 处理 I/O事件的,对于熟悉多线程编程的读者可能会需要关注同步代码。这样的方式不好,因为同步会影响程序的性能,Netty 的设计保证程序处理事件不会有同步。因为某个Channel事件是被添加到一个EventLoop中的,以后该Channel事件都是由该EventLoop来处理的,而EventLoop是一个线程来处理的,也就是说Netty不需要同步IO操作,EventLoop与EventLoopGroup的关系可以理解为线程与线程池的关系一样。
单机版netty
服务端代码
public class NettySever {
public static ChannelGroup channelGroup=new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//获取到pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//向pipeline加入解码器
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
//向pipeline加入编码器
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
//加入自己的业务处理handler
pipeline.addLast(new MyHandler());
}}
)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
ChannelFuture sync = serverBootstrap.bind(8888).sync();
ChannelFuture channelFuture = sync.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
客户端代码
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
NioEventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bootstrap =new Bootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//得到pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//加入相关handler
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
//加入自定义的handler
pipeline.addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println(s);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture sync = bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888)).sync();
Channel channel = sync.channel();
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
while (sc.hasNextLine()){
// System.out.println(sc.next());
channel.writeAndFlush(sc.nextLine());
}
}finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
自定义handle
public class MyhandlerAdapter extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder())
.addLast(new StringEncoder())
.addLast(new MyHandler());
}
}
public class MyHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
// 每一个服务端都可以维护注册在自己上面的channel,当然有些需要自己去维护,比如上线的时候新增,下线删除。也可以自定义一个。
public static ChannelGroup channelGroup=new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 给其他服务端说,某某某上线了
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
ChannelId id = channel.id();
channelGroup.add(channel);
System.out.println(channel.remoteAddress()+"上线了");
channelGroup.forEach(c -> {
if(channel==c){
c.writeAndFlush("我自己上线了");
}else {
c.writeAndFlush(channel.remoteAddress()+"在"+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())+"上线了");
}
});
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 给其他服务端说,某某某上线了
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelGroup.forEach(c -> {
if(channel==c){
c.writeAndFlush("我自己下线了");
}else {
c.writeAndFlush(channel.remoteAddress()+"在"+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())+"下线了");
}
});
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println(s);
Channel channel = channelHandlerContext.channel();
channelGroup.forEach(c -> {
if(channel==c){
c.writeAndFlush(channel.remoteAddress()+"在"+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())+