一、启动脚本分析
独立部署模式下,主要由master和slaves组成,master可以利用zk实现高可用性,其driver,work,app等信息可以持久化到zk上;slaves由一台至多台主机构成。Driver通过向Master申请资源获取运行环境。
启动master和slaves主要是执行/usr/dahua/spark/sbin目录下的start-master.sh和start-slaves.sh,或者执行
start-all.sh,其中star-all.sh本质上就是调用start-master.sh和start-slaves.sh
1.1 start-all.sh
#1.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "`dirname "$0"`"/..; pwd)"
fi
#2.执行${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh,见以下分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh"
#3.执行"${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/start-master.sh,见以下分析
"${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/start-master.sh
#4.执行"${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/start-slaves.sh,见以下分析
"${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/start-slaves.sh
其中start-master.sh和start-slave.sh分别调用的是
org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master和org.apache.spark.deploy.worker.Worker
1.2 start-master.sh
start-master.sh调用了spark-daemon.sh,注意这里指定了启动的类
#1.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "`dirname "$0"`"/..; pwd)"
fi
# NOTE: This exact class name is matched downstream by SparkSubmit.
# Any changes need to be reflected there.
#2.设置CLASS="org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master"
CLASS="org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master"
#3.如果参数结尾包含--help或者-h则打印帮助信息,并退出
if [[ "$@" = *--help ]] || [[ "$@" = *-h ]]; then
echo "Usage: ./sbin/start-master.sh [options]"
pattern="Usage:"
pattern+="\|Using Spark's default log4j profile:"
pattern+="\|Registered signal handlers for"
"${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class $CLASS --help 2>&1 | grep -v "$pattern" 1>&2
exit 1
fi
#4.设置ORIGINAL_ARGS为所有参数
ORIGINAL_ARGS="$@"
#5.执行${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh
. "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh"
#6.执行${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh
. "${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh"
#7.SPARK_MASTER_PORT为空则赋值7077
if [ "$SPARK_MASTER_PORT" = "" ]; then
SPARK_MASTER_PORT=7077
fi
#8.SPARK_MASTER_HOST为空则赋值本主机名(hostname)
if [ "$SPARK_MASTER_HOST" = "" ]; then
case `uname` in
(SunOS)
SPARK_MASTER_HOST="`/usr/sbin/check-hostname | awk '{print $NF}'`"
;;
(*)
SPARK_MASTER_HOST="`hostname -f`"
;;
esac
fi
#9.SPARK_MASTER_WEBUI_PORT为空则赋值8080
if [ "$SPARK_MASTER_WEBUI_PORT" = "" ]; then
SPARK_MASTER_WEBUI_PORT=8080
fi
#10.执行脚本
"${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/spark-daemon.sh start $CLASS 1 \
--host $SPARK_MASTER_HOST --port $SPARK_MASTER_PORT --webui-port $SPARK_MASTER_WEBUI_PORT \
$ORIGINAL_ARGS
其中10肯定是重点,分析之前我们看看5,6都干了些啥,最后直译出最后一个脚本
1.3 spark-config.sh(1.2的第5步)
#判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "`dirname "$0"`"/..; pwd)"
fi
#SPARK_CONF_DIR存在就用此目录,不存在用${SPARK_HOME}/conf
export SPARK_CONF_DIR="${SPARK_CONF_DIR:-"${SPARK_HOME}/conf"}"
# Add the PySpark classes to the PYTHONPATH:
if [ -z "${PYSPARK_PYTHONPATH_SET}" ]; then
export PYTHONPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/python:${PYTHONPATH}"
export PYTHONPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/python/lib/py4j-0.10.6-src.zip:${PYTHONPATH}"
export PYSPARK_PYTHONPATH_SET=1
fi
1.4 load-spark-env.sh(1.2的第6步)
#1.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
#2.判断SPARK_ENV_LOADED是否有值,没有将其设置为1
if [ -z "$SPARK_ENV_LOADED" ]; then
export SPARK_ENV_LOADED=1
#3.设置user_conf_dir为SPARK_CONF_DIR或SPARK_HOME/conf
export SPARK_CONF_DIR="${SPARK_CONF_DIR:-"${SPARK_HOME}"/conf}"
#4.执行"${user_conf_dir}/spark-env.sh" [注:set -/+a含义再做研究]
if [ -f "${SPARK_CONF_DIR}/spark-env.sh" ]; then
# Promote all variable declarations to environment (exported) variables
set -a
. "${SPARK_CONF_DIR}/spark-env.sh"
set +a
fi
fi
# Setting SPARK_SCALA_VERSION if not already set.
#5.选择scala版本,2.11和2.12都存在的情况下,优先选择2.11
if [ -z "$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION" ]; then
ASSEMBLY_DIR2="${SPARK_HOME}/assembly/target/scala-2.11"
ASSEMBLY_DIR1="${SPARK_HOME}/assembly/target/scala-2.12"
if [[ -d "$ASSEMBLY_DIR2" && -d "$ASSEMBLY_DIR1" ]]; then
echo -e "Presence of build for multiple Scala versions detected." 1>&2
echo -e 'Either clean one of them or, export SPARK_SCALA_VERSION in spark-env.sh.' 1>&2
exit 1
fi
if [ -d "$ASSEMBLY_DIR2" ]; then
export SPARK_SCALA_VERSION="2.11"
else
export SPARK_SCALA_VERSION="2.12"
fi
fi
1.5 spark-env.sh
列举很多种模式的选项配置
1.6 spark-daemon.sh
回过头来看看1.2第10步中需要直译出的最后一个脚本,如下:
sbin/spark-daemon.sh start org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master 1 --host hostname --port 7077 --webui-port 8080
上面搞了半天只是设置了变量,最终才进入主角,继续分析spark-daemon.sh脚本
#1.参数个数小于等于1,打印帮助
if [ $# -le 1 ]; then
echo $usage
exit 1
fi
#2.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "`dirname "$0"`"/..; pwd)"
fi
#3.执行${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh,见上述分析 [类似脚本是否有重复?原因是有的人是直接用spark-daemon.sh启动的服务,反正重复设置下变量不需要什么代价]
. "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh"
# get arguments
# Check if --config is passed as an argument. It is an optional parameter.
# Exit if the argument is not a directory.
#4.判断第一个参数是否是--config,如果是取空格后一个字符串,然后判断该目录是否存在,不存在则打印错误信息并退出,存在设置SPARK_CONF_DIR为该目录,shift到下一个参数
#[注:--config只能用在第一参数上]
if [ "$1" == "--config" ]
then
shift
conf_dir="$1"
if [ ! -d "$conf_dir" ]
then
echo "ERROR : $conf_dir is not a directory"
echo $usage
exit 1
else
export SPARK_CONF_DIR="$conf_dir"
fi
shift
fi
#5.分别设置option、command、instance为后面的三个参数(如:option=start,command=org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master,instance=1)
#[注:很多人用spark-daemon.sh启动服务不成功的原因是名字不全]
option=$1
shift
command=$1
shift
instance=$1
shift
#6.日志回滚函数,主要用于更改日志名,如log-->log.1等,略过
spark_rotate_log ()
{
log=$1;
num=5;
if [ -n "$2" ]; then
num=$2
fi
if [ -f "$log" ]; then # rotate logs
while [ $num -gt 1 ]; do
prev=`expr $num - 1`
[ -f "$log.$prev" ] && mv "$log.$prev" "$log.$num"
num=$prev
done
mv "$log" "$log.$num";
fi
}
#7.执行${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh"
#8.判断SPARK_IDENT_STRING是否有值,没有将其设置为$USER(linux用户)
if [ "$SPARK_IDENT_STRING" = "" ]; then
export SPARK_IDENT_STRING="$USER"
fi
#9.设置SPARK_PRINT_LAUNCH_COMMAND=1
export SPARK_PRINT_LAUNCH_COMMAND="1"
# get log directory
#10.判断SPARK_LOG_DIR是否有值,没有将其设置为${SPARK_HOME}/logs,并创建改目录,测试创建文件,修改权限
if [ "$SPARK_LOG_DIR" = "" ]; then
export SPARK_LOG_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/logs"
fi
mkdir -p "$SPARK_LOG_DIR"
touch "$SPARK_LOG_DIR"/.spark_test > /dev/null 2>&1
TEST_LOG_DIR=$?
if [ "${TEST_LOG_DIR}" = "0" ]; then
rm -f "$SPARK_LOG_DIR"/.spark_test
else
chown "$SPARK_IDENT_STRING" "$SPARK_LOG_DIR"
fi
#11.判断SPARK_PID_DIR是否有值,没有将其设置为/tmp
if [ "$SPARK_PID_DIR" = "" ]; then
SPARK_PID_DIR=/tmp
fi
# some variables
#12.设置log和pid
log="$SPARK_LOG_DIR/spark-$SPARK_IDENT_STRING-$command-$instance-$HOSTNAME.out"
pid="$SPARK_PID_DIR/spark-$SPARK_IDENT_STRING-$command-$instance.pid"
# Set default scheduling priority
#13.判断SPARK_NICENESS是否有值,没有将其设置为0 [注:调度优先级,见后面]
if [ "$SPARK_NICENESS" = "" ]; then
export SPARK_NICENESS=0
fi
#14.execute_command()函数,暂且略过,调用时再作分析
execute_command() {
if [ -z ${SPARK_NO_DAEMONIZE+set} ]; then
nohup -- "$@" >> $log 2>&1 < /dev/null &
newpid="$!"
echo "$newpid" > "$pid"
# Poll for up to 5 seconds for the java process to start
for i in {1..10}
do
if [[ $(ps -p "$newpid" -o comm=) =~ "java" ]]; then
break
fi
sleep 0.5
done
sleep 2
# Check if the process has died; in that case we'll tail the log so the user can see
if [[ ! $(ps -p "$newpid" -o comm=) =~ "java" ]]; then
echo "failed to launch: $@"
tail -10 "$log" | sed 's/^/ /'
echo "full log in $log"
fi
else
"$@"
fi
}
#15.进入case语句,判断option值,进入该分支,我们以start为例
# 执行run_command class "$@",其中$@此时为空,经验证,启动带上此参数后,关闭也需,不然关闭不了,后面再分析此参数作用
# 我们正式进入run_command()函数,分析
# I.设置mode=class,创建SPARK_PID_DIR,上面的pid文件是否存在,
# II.SPARK_MASTER不为空,同步删除某些文件
# III.回滚log日志
# IV.进入case,command=org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master,最终执行
# nohup nice -n "$SPARK_NICENESS" "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class $command "$@" >> "$log" 2>&1 < /dev/null &
# newpid="$!"
# echo "$newpid" > "$pid"
# 重点转向bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master
run_command() {
mode="$1"
shift
mkdir -p "$SPARK_PID_DIR"
if [ -f "$pid" ]; then
TARGET_ID="$(cat "$pid")"
if [[ $(ps -p "$TARGET_ID" -o comm=) =~ "java" ]]; then
echo "$command running as process $TARGET_ID. Stop it first."
exit 1
fi
fi
if [ "$SPARK_MASTER" != "" ]; then
echo rsync from "$SPARK_MASTER"
rsync -a -e ssh --delete --exclude=.svn --exclude='logs/*' --exclude='contrib/hod/logs/*' "$SPARK_MASTER/" "${SPARK_HOME}"
fi
spark_rotate_log "$log"
echo "starting $command, logging to $log"
case "$mode" in
(class)
execute_command nice -n "$SPARK_NICENESS" "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class "$command" "$@"
;;
(submit)
execute_command nice -n "$SPARK_NICENESS" bash "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-submit --class "$command" "$@"
;;
(*)
echo "unknown mode: $mode"
exit 1
;;
esac
}
case $option in
(submit)
run_command submit "$@"
;;
(start)
run_command class "$@"
;;
(stop)
if [ -f $pid ]; then
TARGET_ID="$(cat "$pid")"
if [[ $(ps -p "$TARGET_ID" -o comm=) =~ "java" ]]; then
echo "stopping $command"
kill "$TARGET_ID" && rm -f "$pid"
else
echo "no $command to stop"
fi
else
echo "no $command to stop"
fi
;;
(status)
if [ -f $pid ]; then
TARGET_ID="$(cat "$pid")"
if [[ $(ps -p "$TARGET_ID" -o comm=) =~ "java" ]]; then
echo $command is running.
exit 0
else
echo $pid file is present but $command not running
exit 1
fi
else
echo $command not running.
exit 2
fi
;;
(*)
echo $usage
exit 1
;;
esac
1.7 spark-class
#1.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
#2.执行${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/load-spark-env.sh
# Find the java binary
#3.判断JAVA_HOME是否为NULL,不是则设置RUNNER="${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java",否则找系统自带,在没有则报未设置,并退出
if [ -n "${JAVA_HOME}" ]; then
RUNNER="${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java"
else
if [ "$(command -v java)" ]; then
RUNNER="java"
else
echo "JAVA_HOME is not set" >&2
exit 1
fi
fi
# Find Spark jars.
#4.查找SPARK_JARS_DIR,若${SPARK_HOME}/RELEASE文件存在,则SPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/jars",否则
#SPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/assembly/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/jars"
if [ -d "${SPARK_HOME}/jars" ]; then
SPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/jars"
else
SPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/assembly/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/jars"
fi
#5.若SPARK_JARS_DIR不存在且$SPARK_TESTING$SPARK_SQL_TESTING有值[注:一般我们不设置这两变量],报错退出,否则LAUNCH_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_JARS_DIR/*"
if [ ! -d "$SPARK_JARS_DIR" ] && [ -z "$SPARK_TESTING$SPARK_SQL_TESTING" ]; then
echo "Failed to find Spark jars directory ($SPARK_JARS_DIR)." 1>&2
echo "You need to build Spark with the target \"package\" before running this program." 1>&2
exit 1
else
LAUNCH_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_JARS_DIR/*"
fi
# Add the launcher build dir to the classpath if requested.
#6.SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES不是NULL,则LAUNCH_CLASSPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/launcher/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/classes:$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH",
#添加编译相关至LAUNCH_CLASSPATH
if [ -n "$SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES" ]; then
LAUNCH_CLASSPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/launcher/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/classes:$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH"
fi
# For tests
#7.SPARK_TESTING不是NULL,则unset YARN_CONF_DIR和unset HADOOP_CONF_DIR,暂且当做是为了某种测试
if [[ -n "$SPARK_TESTING" ]]; then
unset YARN_CONF_DIR
unset HADOOP_CONF_DIR
fi
#8.build_command函数,略过
build_command() {
"$RUNNER" -Xmx128m -cp "$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH" org.apache.spark.launcher.Main "$@"
printf "%d\0" $?
}
# Turn off posix mode since it does not allow process substitution
set +o posix
CMD=()
while IFS= read -d '' -r ARG; do
CMD+=("$ARG")
#9.最终调用"$RUNNER" -Xmx128m -cp "$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH" org.apache.spark.launcher.Main "$@",
#直译:java -Xmx128m -cp "$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH" org.apache.spark.launcher.Main "$@"
#转向java类org.apache.spark.launcher.Main,这就是java入口类
done < <(build_command "$@")
COUNT=${#CMD[@]}
LAST=$((COUNT - 1))
LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE=${CMD[$LAST]}
# Certain JVM failures result in errors being printed to stdout (instead of stderr), which causes
# the code that parses the output of the launcher to get confused. In those cases, check if the
# exit code is an integer, and if it's not, handle it as a special error case.
if ! [[ $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; then
echo "${CMD[@]}" | head -n-1 1>&2
exit 1
fi
if [ $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE != 0 ]; then
exit $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE
fi
CMD=("${CMD[@]:0:$LAST}")
exec "${CMD[@]}"
1.8 start-slaves.sh
#1.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "`dirname "$0"`"/..; pwd)"
fi
#2.执行${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh"
#3.执行${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh"
# Find the port number for the master
#4.SPARK_MASTER_PORT为空则设置为7077
if [ "$SPARK_MASTER_PORT" = "" ]; then
SPARK_MASTER_PORT=7077
fi
#5.SPARK_MASTER_HOST为空则设置为`hostname`
if [ "$SPARK_MASTER_HOST" = "" ]; then
case `uname` in
(SunOS)
SPARK_MASTER_HOST="`/usr/sbin/check-hostname | awk '{print $NF}'`"
;;
(*)
SPARK_MASTER_HOST="`hostname -f`"
;;
esac
fi
# Launch the slaves
#6.启动slaves,
# "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/slaves.sh" cd "${SPARK_HOME}" \; "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/start-slave.sh" "spark://$SPARK_MASTER_HOST:$SPARK_MASTER_PORT"
# 遍历conf/slaves中主机,其中有设置SPARK_SSH_OPTS,ssh每一台机器执行"${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/start-slave.sh" "spark://$SPARK_MASTER_HOST:$SPARK_MASTER_PORT"
"${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/slaves.sh" cd "${SPARK_HOME}" \; "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/start-slave.sh" "spark://$SPARK_MASTER_HOST:$SPARK_MASTER_PORT"
1.9 转向start-slave.sh
#1.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "`dirname "$0"`"/..; pwd)"
fi
#2.设置CLASS="org.apache.spark.deploy.worker.Worker"
CLASS="org.apache.spark.deploy.worker.Worker"
#3.如果参数结尾包含--help或者-h则打印帮助信息,并退出
if [[ $# -lt 1 ]] || [[ "$@" = *--help ]] || [[ "$@" = *-h ]]; then
echo "Usage: ./sbin/start-slave.sh [options] <master>"
pattern="Usage:"
pattern+="\|Using Spark's default log4j profile:"
pattern+="\|Registered signal handlers for"
"${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class $CLASS --help 2>&1 | grep -v "$pattern" 1>&2
exit 1
fi
#4.执行${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh"
#5.执行${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh"
#6.MASTER=$1,这里MASTER=spark://hostname:7077,然后shift,也就是说单独启动单个slave使用start-slave.sh spark://hostname:7077
MASTER=$1
shift
#7.SPARK_WORKER_WEBUI_PORT为空则设置为8081
if [ "$SPARK_WORKER_WEBUI_PORT" = "" ]; then
SPARK_WORKER_WEBUI_PORT=8081
fi
#8.函数start_instance,略过
function start_instance {
#设置WORKER_NUM=$1
WORKER_NUM=$1
shift
if [ "$SPARK_WORKER_PORT" = "" ]; then
PORT_FLAG=
PORT_NUM=
else
PORT_FLAG="--port"
PORT_NUM=$(( $SPARK_WORKER_PORT + $WORKER_NUM - 1 ))
fi
WEBUI_PORT=$(( $SPARK_WORKER_WEBUI_PORT + $WORKER_NUM - 1 ))
#直译:spark-daemon.sh start org.apache.spark.deploy.worker.Worker 1 --webui-port 7077 spark://hostname:7077
#代码再次转向spark-daemon.sh,见上诉分析
"${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/spark-daemon.sh start $CLASS $WORKER_NUM \
--webui-port "$WEBUI_PORT" $PORT_FLAG $PORT_NUM $MASTER "$@"
}
#9.判断SPARK_WORKER_INSTANCES(可以认为是单节点Worker进程数)是否为空
# 为空,则start_instance 1 "$@"
# 不为空,则循环
# for ((i=0; i<$SPARK_WORKER_INSTANCES; i++)); do
# start_instance $(( 1 + $i )) "$@"
# done
if [ "$SPARK_WORKER_INSTANCES" = "" ]; then
start_instance 1 "$@"
else
for ((i=0; i<$SPARK_WORKER_INSTANCES; i++)); do
#10.转向start_instance函数
start_instance $(( 1 + $i )) "$@"
done
fi
二、其他脚本
2.1 start-history-server.sh
#1.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "`dirname "$0"`"/..; pwd)"
fi
#2.执行${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh"
#3.执行${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh"
#4.exec "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/spark-daemon.sh start org.apache.spark.deploy.history.HistoryServer 1 $@ ,见上诉分析
exec "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/spark-daemon.sh start org.apache.spark.deploy.history.HistoryServer 1 "$@"
2.2 start-shuffle-service.sh
#1.判断SPARK_HOME是否有值,没有将其设置为当前文件所在目录的上级目录
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "`dirname "$0"`"/..; pwd)"
fi
#2.执行${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/spark-config.sh"
#3.执行${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh,见上述分析
. "${SPARK_HOME}/bin/load-spark-env.sh"
#4.exec "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/spark-daemon.sh start org.apache.spark.deploy.ExternalShuffleService 1 ,见上诉分析
exec "${SPARK_HOME}/sbin"/spark-daemon.sh start org.apache.spark.deploy.ExternalShuffleService 1
2.3 start-thriftserver.sh
开启thriftserver,略
三、spark-submit处理逻辑分析
以上主要是介绍了spark启动的一些脚本,这里主要分析一下Spark源码中提交任务脚本的处理逻辑,从spark-submit一步步深入进去看看任务提交的整体流程,首先看一下整体的流程概要图: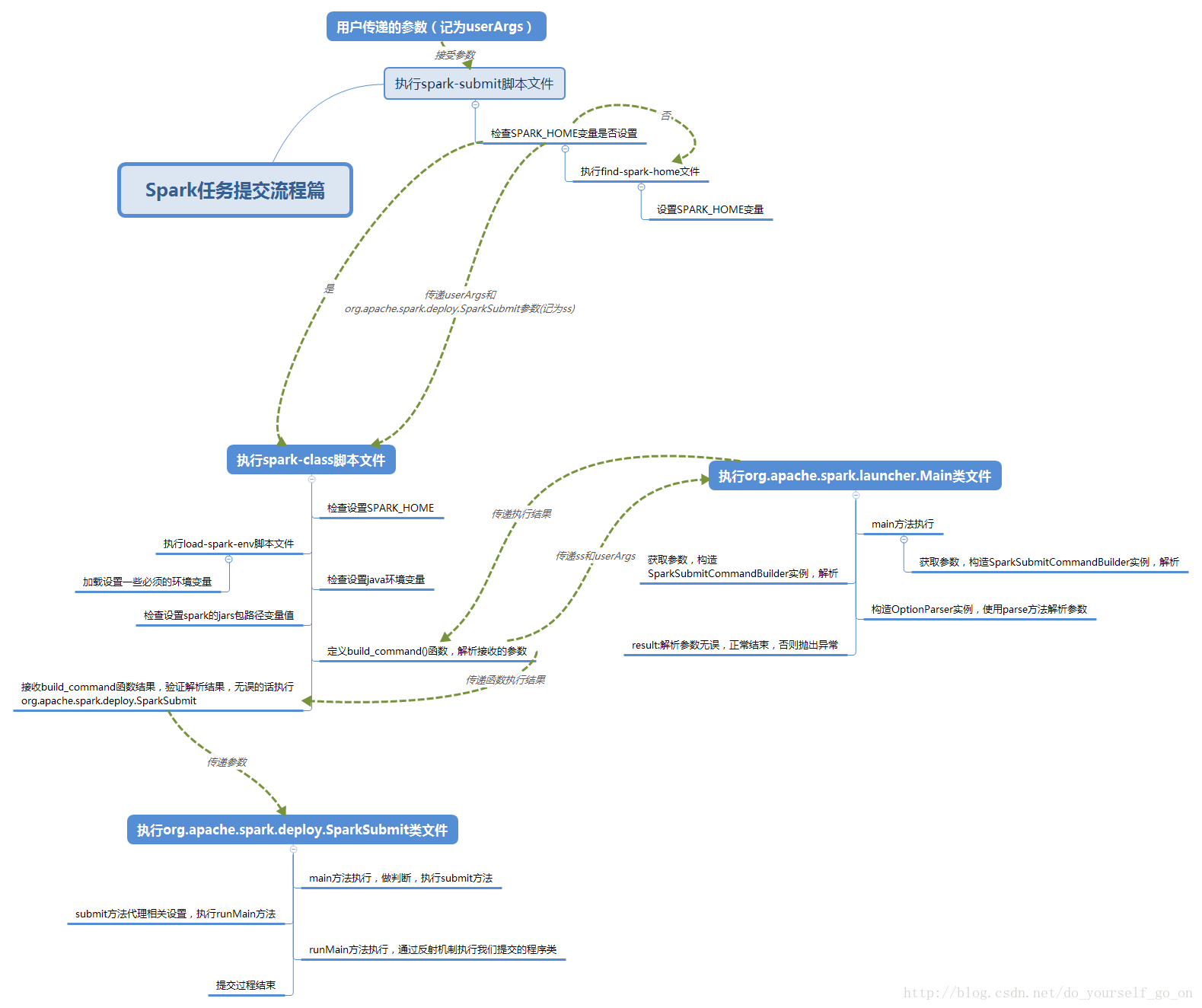
3.1 spark-submit
# -z是检查后面变量是否为空(空则真) shell可以在双引号之内引用变量,单引号不可
#这一步作用是检查SPARK_HOME变量是否为空,为空则执行then后面程序
#source命令: source filename作用在当前bash环境下读取并执行filename中的命令
#$0代表shell脚本文件本身的文件名,这里即使spark-submit
#dirname用于取得脚本文件所在目录 dirname $0取得当前脚本文件所在目录
#$(命令)表示返回该命令的结果
#故整个if语句的含义是:如果SPARK_HOME变量没有设置值,则执行当前目录下的find-spark-home脚本文件,设置SPARK_HOME值
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
# disable randomized hash for string in Python 3.3+
export PYTHONHASHSEED=0
#执行spark-class脚本,传递参数org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit 和"$@"
#这里$@表示之前spark-submit接收到的全部参数
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
所以spark-submit脚本的整体逻辑就是:
首先 检查SPARK_HOME是否设置;if 已经设置 执行spark-class文件 否则加载执行find-spark-home文件
3.2 find-spark-home
#定义一个变量用于后续判断是否存在定义SPARK_HOME的python脚本文件
FIND_SPARK_HOME_PYTHON_SCRIPT="$(cd "$(dirname "$0")"; pwd)/find_spark_home.py"
# Short cirtuit if the user already has this set.
##如果SPARK_HOME为不为空值,成功退出程序
if [ ! -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
exit 0
# -f用于判断这个文件是否存在并且是否为常规文件,是的话为真,这里不存在为假,执行下面语句,给SPARK_HOME变量赋值
elif [ ! -f "$FIND_SPARK_HOME_PYTHON_SCRIPT" ]; then
# If we are not in the same directory as find_spark_home.py we are not pip installed so we don't
# need to search the different Python directories for a Spark installation.
# Note only that, if the user has pip installed PySpark but is directly calling pyspark-shell or
# spark-submit in another directory we want to use that version of PySpark rather than the
# pip installed version of PySpark.
export SPARK_HOME="$(cd "$(dirname "$0")"/..; pwd)"
else
# We are pip installed, use the Python script to resolve a reasonable SPARK_HOME
# Default to standard python interpreter unless told otherwise
if [[ -z "$PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON" ]]; then
PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON="${PYSPARK_PYTHON:-"python"}"
fi
export SPARK_HOME=$($PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON "$FIND_SPARK_HOME_PYTHON_SCRIPT")
fi
可以看到,如果事先用户没有设定SPARK_HOME的值,这里程序也会自动设置并且将其注册为环境变量,供后面程序使用
当SPARK_HOME的值设定完成之后,就会执行Spark-class文件,这也是我们分析的重要部分,源码如下:
3.3 spark-class
#!/usr/bin/env bash
#依旧是检查设置SPARK_HOME的值
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
#执行load-spark-env.sh脚本文件,主要目的在于加载设定一些变量值
#设定spark-env.sh中的变量值到环境变量中,供后续使用
#设定scala版本变量值
. "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/load-spark-env.sh
# Find the java binary
#检查设定java环境值
#-n代表检测变量长度是否为0,不为0时候为真
#如果已经安装Java没有设置JAVA_HOME,command -v java返回的值为${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java
if [ -n "${JAVA_HOME}" ]; then
RUNNER="${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java"
else
if [ "$(command -v java)" ]; then
RUNNER="java"
else
echo "JAVA_HOME is not set" >&2
exit 1
fi
fi
# Find Spark jars.
#-d检测文件是否为目录,若为目录则为真
#设置一些关联Class文件
if [ -d "${SPARK_HOME}/jars" ]; then
SPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/jars"
else
SPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/assembly/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/jars"
fi
if [ ! -d "$SPARK_JARS_DIR" ] && [ -z "$SPARK_TESTING$SPARK_SQL_TESTING" ]; then
echo "Failed to find Spark jars directory ($SPARK_JARS_DIR)." 1>&2
echo "You need to build Spark with the target \"package\" before running this program." 1>&2
exit 1
else
LAUNCH_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_JARS_DIR/*"
fi
# Add the launcher build dir to the classpath if requested.
if [ -n "$SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES" ]; then
LAUNCH_CLASSPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/launcher/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/classes:$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH"
fi
# For tests
if [[ -n "$SPARK_TESTING" ]]; then
unset YARN_CONF_DIR
unset HADOOP_CONF_DIR
fi
# The launcher library will print arguments separated by a NULL character, to allow arguments with
# characters that would be otherwise interpreted by the shell. Read that in a while loop, populating
# an array that will be used to exec the final command.
#
# The exit code of the launcher is appended to the output, so the parent shell removes it from the
# command array and checks the value to see if the launcher succeeded.
#执行类文件org.apache.spark.launcher.Main,返回解析后的参数
build_command() {
"$RUNNER" -Xmx128m -cp "$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH" org.apache.spark.launcher.Main "$@"
printf "%d\0" $?
}
# Turn off posix mode since it does not allow process substitution
#将build_command方法解析后的参数赋给CMD
set +o posix
CMD=()
while IFS= read -d '' -r ARG; do
CMD+=("$ARG")
done < <(build_command "$@")
COUNT=${#CMD[@]}
LAST=$((COUNT - 1))
LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE=${CMD[$LAST]}
# Certain JVM failures result in errors being printed to stdout (instead of stderr), which causes
# the code that parses the output of the launcher to get confused. In those cases, check if the
# exit code is an integer, and if it's not, handle it as a special error case.
if ! [[ $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; then
echo "${CMD[@]}" | head -n-1 1>&2
exit 1
fi
if [ $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE != 0 ]; then
exit $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE
fi
CMD=("${CMD[@]:0:$LAST}")
#执行CMD中的某个参数类org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit
exec "${CMD[@]}"
spark-class文件的执行逻辑稍显复杂,总体上应该是这样的:
检查SPARK_HOME的值—-》执行load-spark-env.sh文件,设定一些需要用到的环境变量,如scala环境值,这其中也加载了spark-env.sh文件——-》检查设定java的执行路径变量值——-》寻找spark jars,设定一些引用相关类的位置变量——》执行类文件org.apache.spark.launcher.Main,返回解析后的参数给CMD——-》判断解析参数是否正确(代表了用户设置的参数是否正确)——–》正确的话执行org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit这个类
3.4 SparkSubmit
2.1最后提交语句,D:\src\spark-2.3.0\core\src\main\scala\org\apache\spark\deploy\SparkSubmit.scala
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
override def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Initialize logging if it hasn't been done yet. Keep track of whether logging needs to
// be reset before the application starts.
val uninitLog = initializeLogIfNecessary(true, silent = true)
//拿到submit脚本传入的参数
val appArgs = new SparkSubmitArguments(args)
if (appArgs.verbose) {
// scalastyle:off println
printStream.println(appArgs)
// scalastyle:on println
}
//根据传入的参数匹配对应的执行方法
appArgs.action match {
//根据传入的参数提交命令
case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs, uninitLog)
//只有standalone和mesos集群模式才触发
case SparkSubmitAction.KILL => kill(appArgs)
//只有standalone和mesos集群模式才触发
case SparkSubmitAction.REQUEST_STATUS => requestStatus(appArgs)
}
}
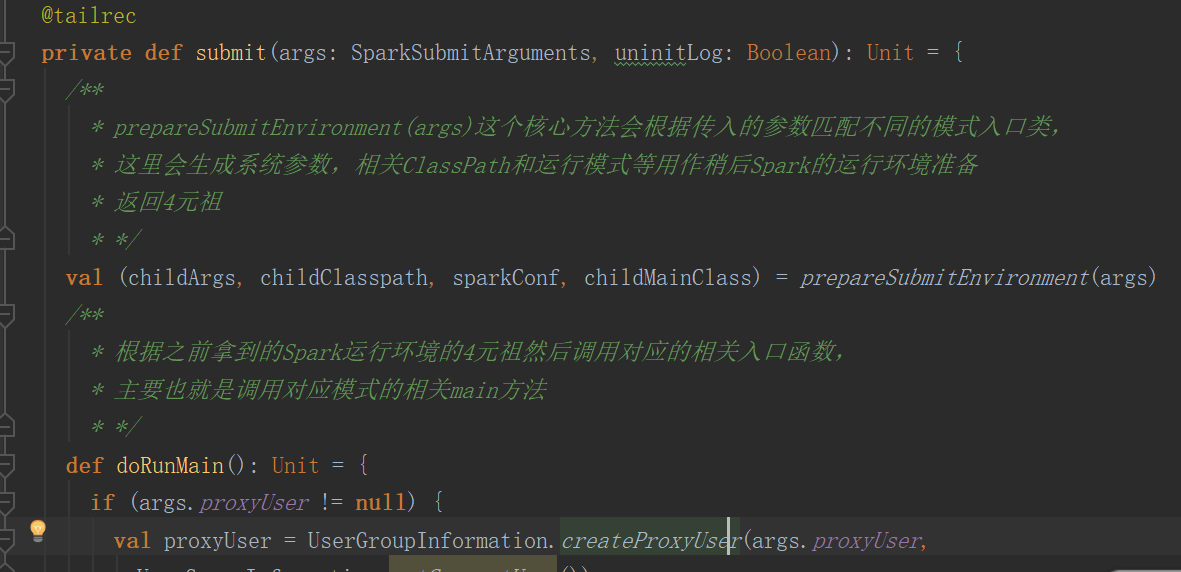
3.4.1 submit十分关键,主要分为两步骤
(1)调用prepareSubmitEnvironment
(2)调用doRunMain